I’m a final year PhD student at CMU advised by Prof. Zico Kolter and Prof. Zac Manchester. Developing RL and iterated inference based reasoning algorithms for deep networks across applications spanning multi-agent LLMs, robotic control, 3D vision, generative models and differentiable solvers. Published at NeurIPS, CVPR, CoRL, ICRA, AAMAS. Blending deep algorithmic understanding with pragmatic engineering to deliver robust, reliable systems. My publications and descriptions of some selected projects are available below and on my Google Scholar page.
I also carely deeply about ensuring that we build AI that benefits humanity and ensuring our social infrastructure can adapt to it. I’ve written various blogs discussing my thoughts on various topics, from ‘the economic and governance infrastructure for the agentic web’ to ‘where the next scaling laws for LLMs will come from’. Follow my Blog.
| August 2020 - Present |
Ph.D. in Robotics Research
(0.00/0.00)
Carnegie Mellon University |
| Aug 2017 - Dec 2019 |
M.S. in Robotics Research
(4.09/4.33)
Carnegie Mellon University |
| July 2013 - May 2017 |
B.S. in Electrical Engineering
(8.99/10.00)
IIT-BHU Varanasi |
 |
Scaffolding of Trust : Reimagining Economics and Governance for the Agentic Web Swaminathan Gurumurthy, J Zico Kolter, Zachary Manchester To be submitted to ICLR 2026 Blogs [1] [Blog] We discuss the economic and governance tools and frameworks required for the emerging AI-driven internet. We propose various tools and mechanisms to this end such as multi-sided reputation markets, agentic marketplaces, attribution-led pricing, auction-first markets, and a framework for polycentric governance and the tools required. |
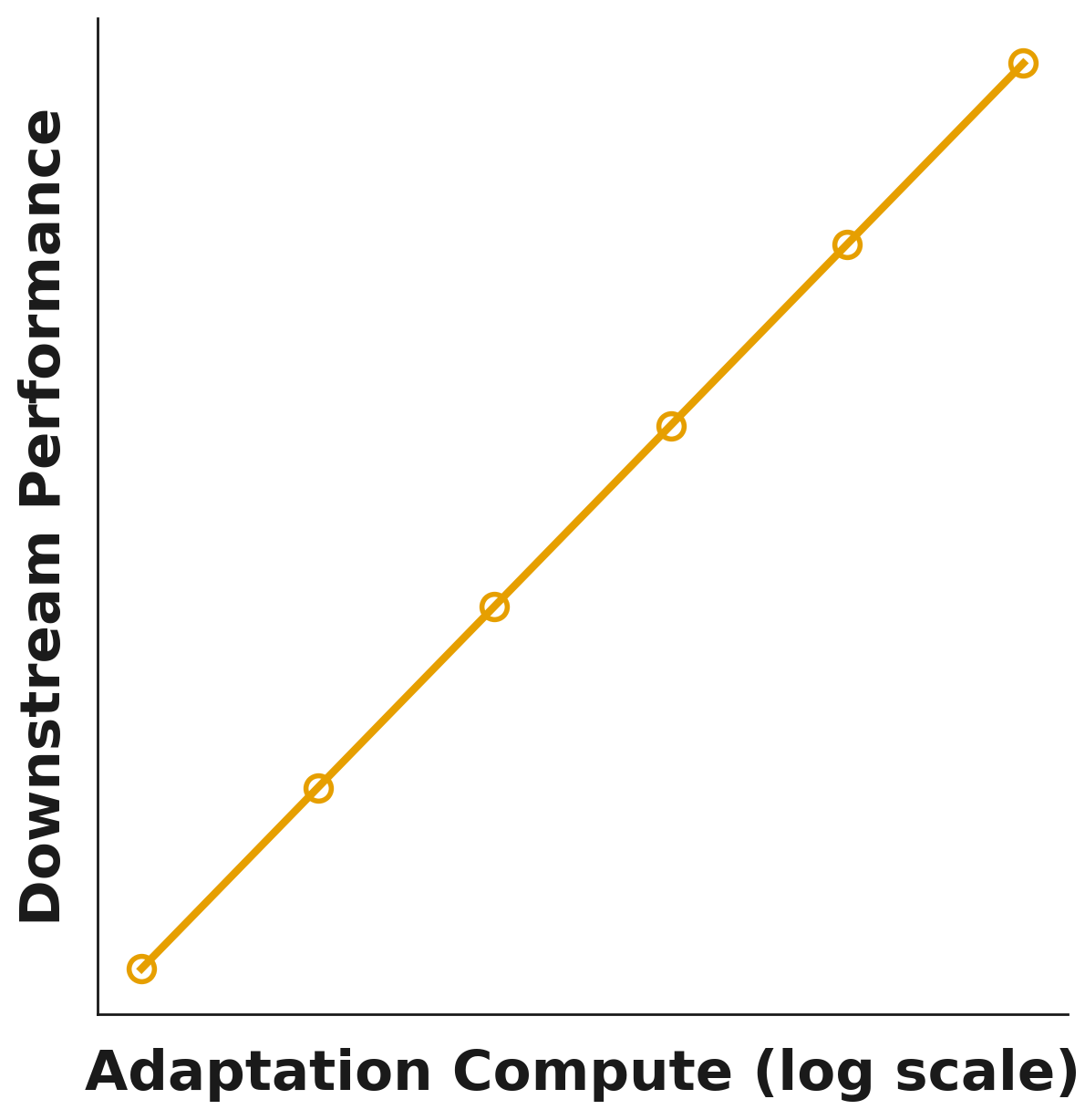 |
Meta-Learning and Learning to Search : The Next Scaling Laws Swaminathan Gurumurthy, J Zico Kolter, Zachary Manchester To be submitted to ICLR 2026 Blogs [1] [Blog] While data scaling and test-time compute built today's AI systems, the next generation will be defined by two new scaling laws hiding in plain sight: parallel search and meta-learning. This article explores how training models to perform native parallel reasoning and to reliably fine-tune themselves on specialized tasks could transform ad-hoc techniques into capital-absorbing scaling laws with predictable performance gains and qualititively new capabilities—from static knowledge artifacts to dynamic systems capable of autonomous exploration and specialized adaptation. |
 |
Trust Markets : Market based Reputation System for Multi-Agent LLM Platforms Swaminathan Gurumurthy, J Zico Kolter, Zachary Manchester In Progress (ICML 2026) [1] [Blog] We co-design and implement a market based reputation system and the corresponding scaffolding for LLM agents. The reputation system serves as a dynamic alignment system for LLM agent platforms where different agent providers compute for better reputation and trust. We further investigate various elements of the LLM scaffolding that are important including, computing iterated equilibria to reach faster and stable equilibria, using optimization based investing as tools for the LLMs and bayesian averaging of the LLM preferences over time to ensure the stability of the preferences and the equilibrium. |
 |
Trust Markets : Market based Reputation System for Multi-Agent LLM Platforms Swaminathan Gurumurthy, J Zico Kolter, Zachary Manchester In Progress (ICML 2026) [1] [pdf] [code] We co-design and implement a market based reputation system and the corresponding scaffolding for LLM agents. The reputation system serves as a dynamic alignment system for LLM agent platforms where different agent providers compute for better reputation and trust. We further investigate various elements of the LLM scaffolding that are important including, computing iterated equilibria to reach faster and stable equilibria, using optimization based investing as tools for the LLMs and bayesian averaging of the LLM preferences over time to ensure the stability of the preferences and the equilibrium. |
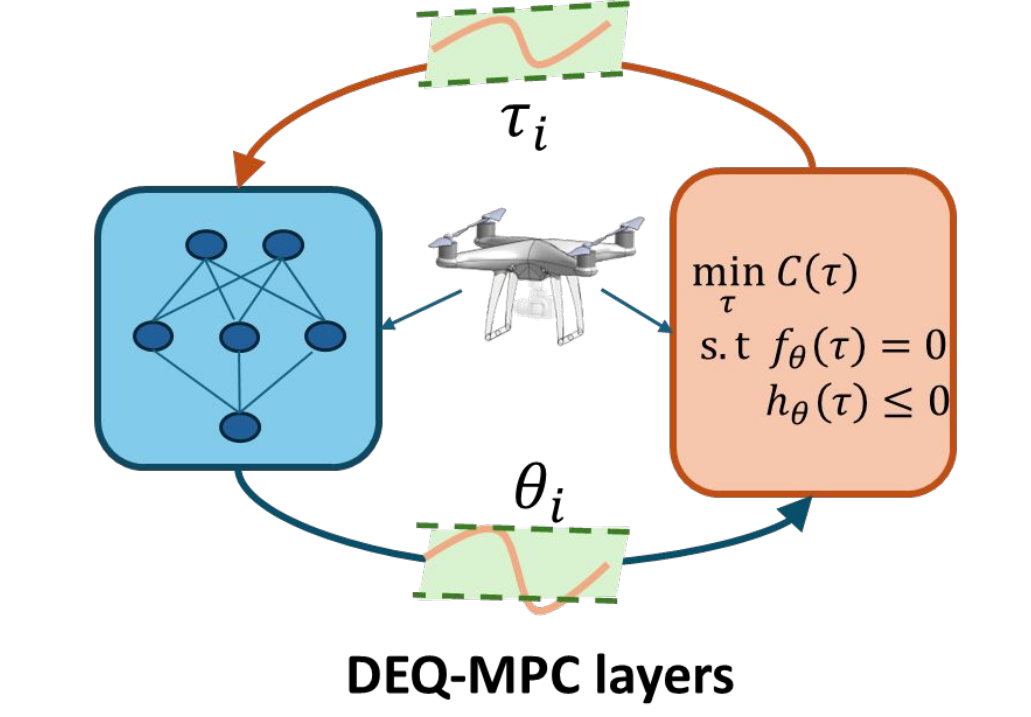 |
DEQ-MPC : Deep Equilibrium Model Predictive Control Swaminathan Gurumurthy, Khai Nguyen, Arun L Bishop, J Zico Kolter, Zachary Manchester CoRL 2025 [1] [pdf] [code] We propose a novel approach that co-develops the solver and architecture unifying the optimization solver and network inference problems. Specifically, we formulate this as a \textit{joint fixed-point problem} over the coupled network outputs and necessary conditions of the optimization problem. Through extensive ablations in various robotic control tasks, we demonstrate that our approach results in richer representations and more stable training, while naturally accommodating warm starting, a key requirement for optimal control problems. |
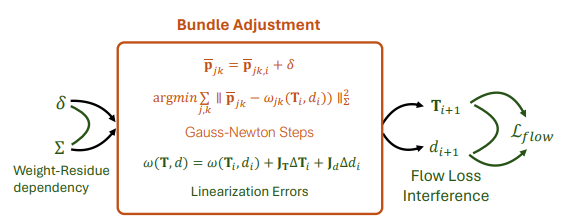 |
From Variance to Veracity: Unbundling and Mitigating Gradient Variance in Differentiable Bundle Adjustment Layers Swaminathan Gurumurthy, Karnik Ram, Bingqing Chen, Zachary Manchester, Zico Kolter CVPR 2024 [1] [pdf] [code] We identify/show three causes for gradient instability and gradient variance when using differentiable bundle adjustment layers within iterative refinement models : (1) flow loss interference, (2) linearization errors in the bundle adjustment (BA) layer, and (3) dependence of weight gradients on the BA residual. We then propose a simple, yet effective solution to reduce the gradient variance by using the weights predicted by the network in the inner optimization loop to weight the correspondence objective in the training problem. |
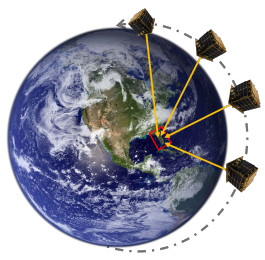 |
VINSat: Solving the Lost-in-Space Problem with Visual-Inertial Navigation Kyle McCleary, Swaminathan Gurumurthy, Paulo RM Fisch, Saral Tayal, Zachary Manchester, Brandon Lucia ICRA 2024 [1] [pdf] [code] This paper introduces a solution to this “lost-in-space” problem that we call Visual Inertial Navigation for Satellites (VINSat). VINSat performs OD using data from an inertial measurement unit (IMU) and a low-cost RGB camera. We train an object detector to detect landmarks on the earth's surface and then solve a batch optimization problem for state estimation of the satellite given the detected landmarks. |
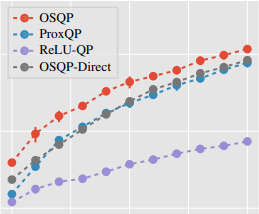 |
ReLU-QP: A GPU-Accelerated Quadratic Programming Solver for Model-Predictive Control Arun L. Bishop*, John Z. Zhang*, Swaminathan Gurumurthy, Kevin Tracy, Zachary Manchester ICRA 2024 [1] [pdf] [code] We present ReLU-QP, a GPU-accelerated solver for quadratic programs (QPs) that is capable of solving high-dimensional control problems at real-time rates. ReLU-QP is derived by exactly reformulating the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM) algorithm for solving QPs as a deep, weight-tied neural network with rectified linear unit (ReLU) activations. This reformulation enables the deployment of ReLU-QP on GPUs using standard machine-learning toolboxes. |
 |
SLoMo: A General System for Legged Robot Motion Imitation from Casual Videos John Z. Zhang, Shuo Yang, Gengshan Yang, Arun L. Bishop, Swaminathan Gurumurthy, Deva Ramanan, Zachary Manchester RA-L 2023 [1] [pdf] [code] We present SLoMo: a first-of-its-kind framework for transferring skilled motions from casually captured "in the wild" video footage of humans and animals to legged robots. SLoMo works in three stages: 1. synthesize a physically plausible reconstructed key-point trajectory from monocular videos; 2. optimize a dynamically feasible reference trajectory for the robot offline that includes body and foot motion, as well as contact sequences that closely tracks the key points; 3. track the reference trajectory online using a general-purpose model-predictive controller on robot hardware |
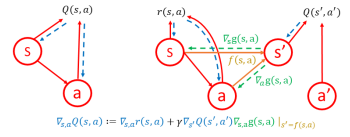 |
Deep Off-Policy Iterative Learning Control Swaminathan Gurumurthy, Zico Kolter, Zachary Manchester L4DC 2023 [1] [pdf] [code] The paper proposes an update equation for the value-function gradients to speed up actor critic methods in reinforcement learning. This update is inspired by iterative learning control (ILC) approaches that use approximate simulator gradients to speed up optimization. The value-gradient update leads to a significant improvement in sample efficiency and sometimes better performance both when learning from scratch or fine-tuning a pre-trained policy in a new environment. |
 |
Practical Critic Gradient based Actor Critic for On-Policy Reinforcement Learning Swaminathan Gurumurthy, Zachary Manchester, Zico Kolter L4DC 2023 [1] [pdf] [code] In this paper, we present a different class of on-policy algorithms based on SARSA, which estimate the policy gradient using the critic-action gradients. We show that they are better suited than existing baselines (like PPO) especially when using highly parallelizable simulators. We observe that the critic gradient based on-policy method (CGAC) consistently achieves higher episode returns. Furthermore, in environments with high dimensional action space, CGAC also trains much faster (in wall-clock time) than the corresponding baselines. |
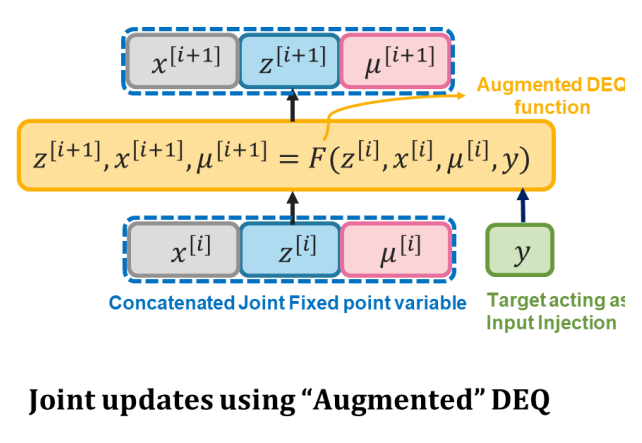 |
Joint inference and input optimization in equilibrium networks Swaminathan Gurumurthy, Shaojie Bai, Zachary Manchester, Zico Kolter Neurips 2021 [1] [pdf] [code] We propose to use Deep Equilibrium Models to solve inverse problems efficiently by exploiting the iterative nature of the DEQ fixed point process. We simultaneously solve for the DEQ fixed point and optimize over network inputs, all within a single augmented DEQ model that jointly encodes both the original network and the optimization process. Indeed, the procedure is fast enough that it allows us to efficiently train DEQ models for tasks traditionally relying on an inner optimization loop. |
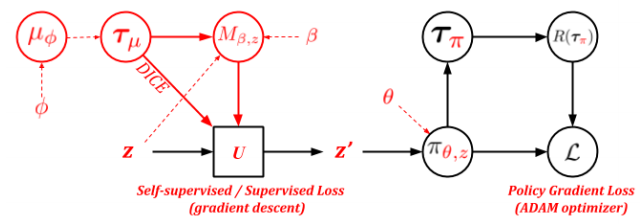 |
MAME : Model Agnostic Meta Exploration Swaminathan Gurumurthy, Sumit Kumar, Katia Sycara CoRL 2019 [1] [pdf] [code] We propose to explicitly model a separate exploration policy for the task distribution in Meta-RL given the requirements on sample efficiency. Having two different policies gives more flexibility during training and makes adaptation to any specific task easier. We show that using self-supervised or supervised learning objectives for adaptation stabilizes the training process and improves performance. |
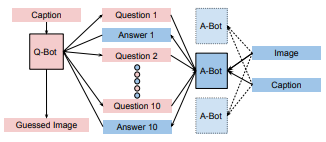 |
Community Regularization of Visually-Grounded Dialog Akshat Agarwal*, Swaminathan Gurumurthy*, Vasu Sharma*, Katia Sycara, Michael Lewis AAMAS 2019 [Oral talk] [2] [pdf] [code] We aim to train 2 agents on the visual dialogue dataset where one agent is given access to an image and the other agent is tasked with guessing the contents of the image by establishing a dialogue with the first agent. The two agents are initially trained using supervision followed by Reinforce. In order to combat the resulting drift from natural language when training with Reinforce, we introduce a community regularization scheme of training a population of agents. |
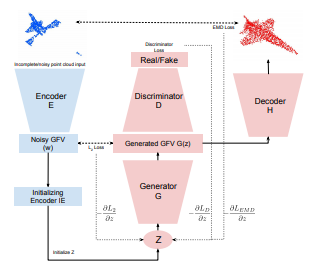 |
3D Point Cloud Completion using Latent Optimization in GANs Shubham Agarwal*, Swaminathan Gurumurthy* WACV 2019 [3] [pdf] We address a fundamental problem with Neural Network based point cloud completion methods which reconstruct the entire structure rather than preserving the points already provided as input. These methods struggle when tested on unseen deformities. We address this problem by introducing a GAN based Latent optimization procedure to perform output constrained optimization using the regions provided in the input. |
 |
Exploiting Data and Human Knowledge for Predicting Wildlife Poaching Swaminathan Gurumurthy, Lantao Yu, Chenyan Zhang, Yongchao Jin, Weiping Li, Haidong Zhang, Fei Fang COMPASS 2019 [Oral talk] [4] [pdf] [code] Using past data of traps/snares found in a wildlife Sanctuary, we predict the regions of high probability of traps/snares to guide the rangers to patrol those regions. We use novel frameworks of incorporating expert domain knowledge for the dynamic sampling of data points in order to tackle the imbalance in data. We further use these regions to produce optimal patrol routes for the rangers. This has now been deployed in a conservation area in China. |
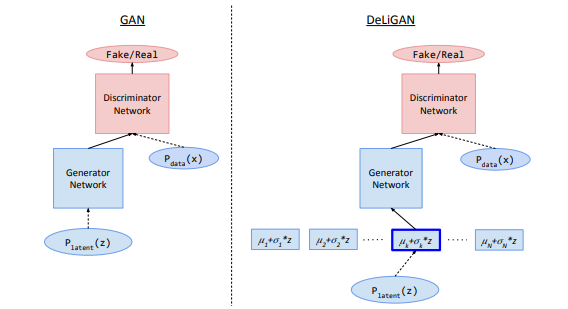 |
DeLiGAN: GANs for Diverse and Limited Data Swaminathan Gurumurthy*, Ravi Kiran S.* and R. Venkatesh Babu CVPR 2017 [5] [pdf] [code] We try to explore the idea of finding high probability regions in the latent space of GANs by learning a latent space representation using learnable Mixture of Gaussians. This enables the GAN to model a multimodal distribution and stabilizes training as observed visually and by the intra-class variance measured using a modified inception score. Our modification is especially useful when the dataset is very small and diverse. |
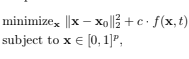 |
Query Efficient Black Box Attacks in Neural Networks Swaminathan Gurumurthy, Fei Fang and Martial Hebert [6] [pdf] We test various methods to increase the sample efficiency of adversarial black box attacks on Neural nets. In one of the methods, we analyze the transferability of gradients and find that it has two components: Network specific components and Task specific components. The task specific component corresponds to the transferable properties of adversarial examples between architectures. Hence, we attempted to isolate this component and enhance the transfer properties. We then perform multiple queries on the black box network to obtain the architecture specific components using ES. |
 |
Visual SLAM based SfM for Boreholes Swaminathan Gurumurthy, Tat-Jun Chin and Ian Reid [7] [code] Built a package to construct a sparse map and camera trajectory using SIFT features, fine-tuned using bundle adjustment and loop closure. It was tailored for boreholes and underground scenes with forward motion, where most of the current state of the art approaches like LSD SLAM, ORB SLAM and SVO struggled at both localization and mapping. |
 |
Off-on policy learning Swaminathan Gurumurthy, Bhairav Mehta, Anirudh Goyal [8] On policy methods are known to exhibit stable behavior and off-policy methods are known to be sample efficient. The goal here was to get the best of both worlds. We first developed a self-imitation based method to learn from a diverse set of exploratory policies which perform coordinated exploration. We also tried a meta-learning objective to ensure that the off-policy updates to the policies are aligned with future on-policy updates. This leads to more stable training but fails to reach peak performance in most continuous control tasks we tested on. |
 |
Exploring interpretability in Atari Games for RL policies using Counterfactuals Swaminathan Gurumurthy, Akshat Agarwal, Prof. Katia Sycara [9] We aimed to understand what RL agents learn in simple games such as in Atari. We developed a GAN based method to find counterfactuals for the policies, i.e., we find small perturbations in the scene that can lead to changes in the agent action and use these to interpret agent behavior. GAN in this case is used to avoid adversarial examples and produce semantically meaningful perturbations. |
Last updated on 2020-06-13